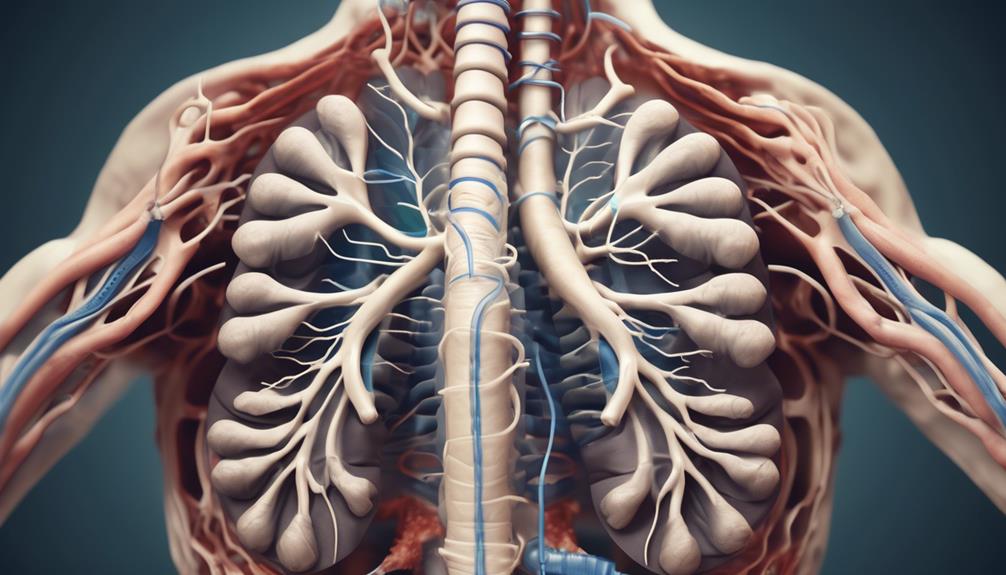
The intricate workings of a cat's respiratory system are often overlooked, yet they play a crucial role in the feline's overall health and well-being. Understanding the nuances of how a cat breathes, filters air, and exchanges gases provides valuable insights into their physiological functions.
As we delve into the six key insights into the cat respiratory system, we will uncover the fascinating mechanisms that enable these graceful creatures to thrive in their environment.
Key Takeaways
- The nasal cavity plays a crucial role in filtering airborne particles and pathogens, reducing the risk of respiratory infections.
- The larynx regulates airflow, protects the airway, and assists in controlling airflow and protecting respiratory tissues.
- The trachea facilitates air passage, prevents collapse with cartilage rings, and optimizes oxygen exchange and carbon dioxide removal.
- The bronchial tree facilitates air passage into the lungs, maximizes surface area for efficient gas exchange, and understanding its function aids in diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases.
Nasal Cavity and Air Filtration
The nasal cavity plays a crucial role in the cat's respiratory system, serving as the primary site for air filtration and humidification. It is lined with specialized cells that trap airborne particles, pathogens, and allergens, preventing them from reaching the lower respiratory tract. This filtration process is essential in reducing the risk of respiratory infections in cats. Additionally, the nasal cavity is responsible for humidifying the inhaled air, ensuring that it reaches the lungs at the optimal humidity level for efficient gas exchange.
In addition to its role in air filtration and humidification, the nasal cavity also contributes to the cat's olfactory function. The olfactory epithelium, located in the nasal cavity, contains sensory cells that enable cats to detect and distinguish various odors. This acute sense of smell is crucial for hunting, identifying territory, and social interactions.
Furthermore, the nasal cavity is intricately connected to the respiratory system, and any issues within it can impact the overall respiratory health of the cat. Therefore, maintaining the nasal cavity's health and function is essential in ensuring the well-being of the feline respiratory system.
Role of the Larynx in Breathing
Playing a crucial role in the feline respiratory system, the larynx serves as a specialized structure involved in regulating airflow, protecting the airway, and producing vocalizations.
The larynx, situated at the junction of the pharynx and the trachea, functions as a valve to control the passage of air into the respiratory system.
During breathing, the larynx opens to allow air to pass freely into the trachea and lungs. This process is crucial in maintaining a steady flow of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
Additionally, the larynx contains the vocal cords, which play a significant role in producing sounds for communication.
In the event of foreign object entry, the larynx acts as a protective mechanism, triggering the cough reflex to expel the intruder and prevent it from entering the lower respiratory tract.
The larynx also contributes to the overall breathing mechanism by assisting in the control of airflow and protecting the delicate tissues of the lower respiratory system.
Understanding the multifaceted functions of the larynx is essential in diagnosing and treating respiratory disorders in cats.
The Importance of the Trachea
Serving as a continuation of the discussion on respiratory system functionality, the trachea in cats plays a vital role in facilitating the passage of air from the larynx into the lungs and expelling foreign particles to maintain respiratory health. The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a rigid tube composed of cartilage rings, which prevent it from collapsing and obstructing airflow. It is situated anterior to the esophagus and extends from the larynx to the bronchi, where it branches to enter the lungs. The tracheal anatomy is designed to optimize airflow, allowing for efficient oxygen exchange and the removal of carbon dioxide.
Breathing mechanics in cats rely on the trachea's ability to maintain airway patency. The cartilage rings provide structural support, ensuring that the trachea remains open during both inhalation and exhalation. Additionally, the tracheal epithelium is lined with cilia and mucus-producing cells that trap and sweep away inhaled particles and microorganisms, preventing them from reaching the delicate lung tissue. This defense mechanism is crucial for preventing respiratory infections and maintaining optimal lung function.
Understanding the importance of the trachea in cats is essential for veterinary professionals and pet owners alike. By recognizing its role in facilitating proper breathing and protecting the respiratory system from harmful substances, individuals can take proactive measures to safeguard feline respiratory health.
Function of the Bronchial Tree
Functioning as a complex network of airways within the cat's respiratory system, the bronchial tree serves a critical role in facilitating the passage of air into the lungs and optimizing gas exchange. The bronchial tree is composed of the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. The bronchi are the main airways leading into the lungs, which further divide into smaller bronchioles. These bronchioles then terminate in the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs. The structure of the bronchial tree is designed to maximize the surface area available for gas exchange, allowing for efficient oxygenation of the blood and removal of carbon dioxide.
Understanding the function of the bronchial tree is essential in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory system diseases in cats. Diseases such as feline asthma, bronchitis, and lung infections can affect the bronchial tree, leading to symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. By comprehending the normal function of the bronchial tree, veterinarians can better assess and manage these conditions, ultimately improving the respiratory health and overall well-being of feline patients.
Gas Exchange in the Alveoli
Gas exchange in the alveoli, which is integral to the respiratory process, is the crucial mechanism by which oxygen is taken up from inhaled air and carbon dioxide is released from the blood into the lungs.
Alveoli are the primary sites for gas exchange in the lungs and are well-suited for this function due to their unique structure. The alveolar structure consists of a single layer of thin, squamous epithelial cells, allowing for rapid diffusion of gases. This thin barrier facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries.
Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses through the alveolar walls and into the pulmonary capillaries, where it binds to hemoglobin for transport to the body's tissues. Conversely, carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli to be exhaled. This exchange is facilitated by the extensive network of pulmonary capillaries surrounding the alveoli, known as the pulmonary circulation.
The efficient functioning of the alveoli is vital for maintaining proper oxygen levels in the blood and removing carbon dioxide, ensuring the respiratory needs of the body are met.
Respiratory Control and Regulation
Respiratory control and regulation encompass the intricate coordination of neural and chemical mechanisms to maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the body, ensuring optimal function of the respiratory system.
The respiratory regulation primarily involves the brainstem, which contains specialized respiratory centers that regulate the rate and depth of breathing in response to changing oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
Chemoreceptors, located in the arteries, monitor the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in the blood, providing essential feedback to the respiratory centers to adjust breathing accordingly.
Additionally, the transport of oxygen in the blood is regulated by factors such as hemoglobin concentration, blood flow, and the efficiency of gas exchange in the lungs. Similarly, carbon dioxide transport is tightly regulated through the formation of bicarbonate ions and the binding of carbon dioxide to hemoglobin.
This intricate regulatory system ensures that the body's tissues receive adequate oxygen and that waste carbon dioxide is efficiently removed, maintaining the delicate balance required for optimal cellular function.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Cats Develop Respiratory Illnesses From Exposure to Secondhand Smoke?
Yes, cats can develop respiratory illnesses from exposure to secondhand smoke. Secondhand smoke can lead to feline respiratory issues, allergies, and other related health problems. It is important to keep cats away from smoking environments to safeguard their health.
What Role Do Allergies Play in Causing Respiratory Issues in Cats?
Allergies can trigger respiratory symptoms in cats, leading to discomfort and health issues. Treatment options include medication and environmental changes. Prevention strategies involve managing air quality, humidity levels, and reducing stress and anxiety triggers.
Are There Any Specific Breathing Exercises or Techniques That Can Improve a Cat's Respiratory Health?
Breathing techniques and respiratory exercises can benefit a cat's respiratory health. Techniques such as controlled breathing, environmental adaptations, and exercise can improve lung function, alleviate breathing difficulties, and enhance overall respiratory well-being in cats.
How Does a Cat's Respiratory System Adapt or Change During Times of Stress or Anxiety?
The feline respiratory system responds to stress by triggering a "fight or flight" response, increasing respiratory rate and depth. Anxiety may cause shallow, rapid breathing. These adaptations help prepare the cat for potential danger and aid in survival.
Are There Any Specific Environmental Factors That Can Impact a Cat's Respiratory Function, Such as Air Quality or Humidity Levels?
Indoor pollutants such as smoke, dust, and volatile organic compounds can impact a cat's respiratory function, leading to respiratory issues. Additionally, climate factors like humidity levels can also influence a cat's respiratory health. Understanding these environmental factors is crucial for promoting feline respiratory wellness.